The module - in brief
The purpose of this module is to support a systematic dialogue on prioritising building blocks for cyber security.
Key individuals collectively assess the practical implications of the building block analyses and determine the initial steps in further developing cyber security.
The result is a clear understanding of what is important here and now, and what will follow later.
Prerequisite for using the tool:
The company must have completed either the work sheets linked to Situational analysis of building blocks for cyber security, or the work sheets linked to Building blocks for cyber security so that it is clear what should be prioritised.
Prioritising actions
Assessing how new knowledge and insights translate into practical actions can pose a challenge. One wants to utilise the new knowledge but doesn’t know where and how to start.
The prioritisation dialogue provides a structured reflection process that serves as a starting point for acting based on the knowledge about the company’s cyber security. It focuses on determining the sequence of actions, rather than excluding actions.
Prioritising building blocks for cybersecurity
The prioritisation tool is a simple dialogue guide with three types of questions:
The purpose of the questions is to guide the company in prioritising a specific building block for cyber security, which represents the cyber security task that needs to be addressed first.
The three types of questions cover the following topics across all four building blocks:
- the company’s perspectives on the current cyber security status, and the reasons behind it.
- the company’s opportunities and challenges in further developing cyber security.
- the company’s prioritisation of the upcoming cyber security tasks.
Structuring the dialogue about prioritisation
It may seem cumbersome, but it is very important to stick to the structure of the dialogue.
The purpose of the structure is to look into the previous analysis of the current status of cyber security before the company begins to act to further develop cyber security.
The reflection process built into the dialogue includes the following three steps where participants move from one perspective on the current status of cyber security, to reflecting on the opportunities and challenges for further developing cyber security, and finally prioritising one building block for cyber security over the others.
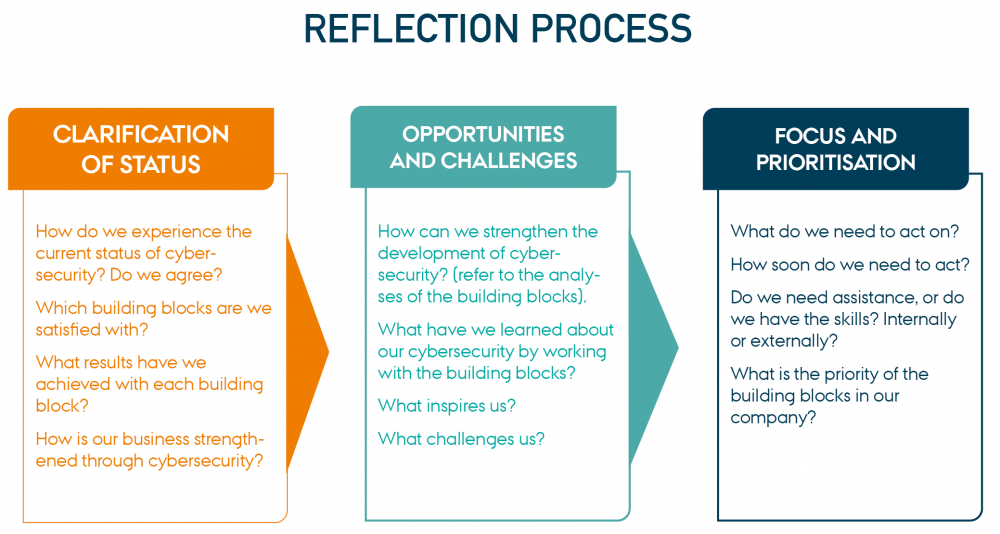
“Reflection Process” from CyPro under licens CC BY-SA 4.0
Practical information
- Invite employees and managers who have participated in the previous analyses of the building blocks and who have decision-making power and knowledge of cyber security.
- It is beneficial if knowledge about all four building blocks is represented at the meeting.
- Schedule a meeting with a duration of approx. 1 hour for the prioritisation dialogue.
- Provide each participant with a paper ‘kit’ of the company’s completed analyses sheets (situational analyses or idea catalogues).
- A manager/the meeting organiser prepares a brief oral summary of the previous analyses as an introduction to the dialogue.
Step-by-step
Step by step guide
1) Present the prepared summary of the previous analyses of the building blocks (5 minutes).
2) Start by discussing the questions under Clarification of status - it is not necessary to take notes (15 minutes). Begin with the question: how do we experience the current status of cybersecurity in the company?
3) Proceed to Opportunities and challenges. During your discussion, you can elaborate on the insights from the clarification of status. It is not necessary to take notes (15 minutes).
4) Finally, the participants go through all the questions in the column Focus and prioritisation (20 minutes).
a) For the last question (what is the priority of the building blocks?), place a paper copy of each of the four completed analyses of the building blocks on the meeting table. Dedicate the rest of the meeting to prioritise them, where no. 1 is the most important building block for cyber security in the company right now.
b) It should be done as a collaborative physical prioritisation of the completed sheets from the analyses of the building blocks. It can be beneficial if the participants stand up around the table.
5) Write down the sequence of the building blocks for cyber security and send them to the participants as a summary of the dialogue.
Outcome
Based on the prioritisation dialogue, you now have a clear picture of the significance and impact of the building blocks in your company. The dialogue prepares you to act on cyber security through your own interpretation of what the building blocks mean in your specific context.
Additionally, the dialogue also facilitates internal knowledge sharing and contributes to establishing a common language for cyber security.
Based on the collective prioritisation, you now need to formulate a goal for the prioritised building block to ensure that the upcoming actions are clear and well-defined for everyone in the company.
Expert advice
Instead of perceiving cybersecurity development as a task to be carried out by a single individual, having a common language and consensus about prioritised cybersecurity actions increases the company’s awareness of cybersecurity and strengthens discussions.
It is important to realise that specific goals for the next steps can only be defined, once the building blocks have been prioritised. This enables the cybersecurity team to make concrete and inspiring goals based on tangible content.
Next step
The next step is to define a specific action and an expected goal for the action – both related to the building block with the highest priority. The tool Goal for the selected building block for cyber security can be used.

The contents described above have been developed in the project:
’CyPro – Cybersecure manufacturing in Denmark’ by Aarhus University, Alexandra Institut, DAMRC, UGLA Insights and FORCE Technology funded by The Danish Industry Foundation. Material from the project is published under licence CC BY-SA 4.0



