
June 2, 2023
Before you start
This learning module is part of the building block:
The module - in brief
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to physical devices (e.g. vehicles, buildings, and other objects) that are equipped with sensors, software, and network connectivity, enabling them to collect and exchange data. With the rapid growth in the number of IoT devices, the number of risks and vulnerabilities associated with these devices increases. To mitigate these threats, it is important to establish basic cybersecurity measures that can protect the devices against cyber-attacks and unauthorized access. This module presents the key components of baseline cybersecurity for IoT and provides examples of best practices for securing IoT devices.
Basic IoT security
To gain a deeper understanding of basic IoT security, it is important to understand these four main components: IoT characteristics, IoT security challenges, IoT security risks, and best practices for IoT security.
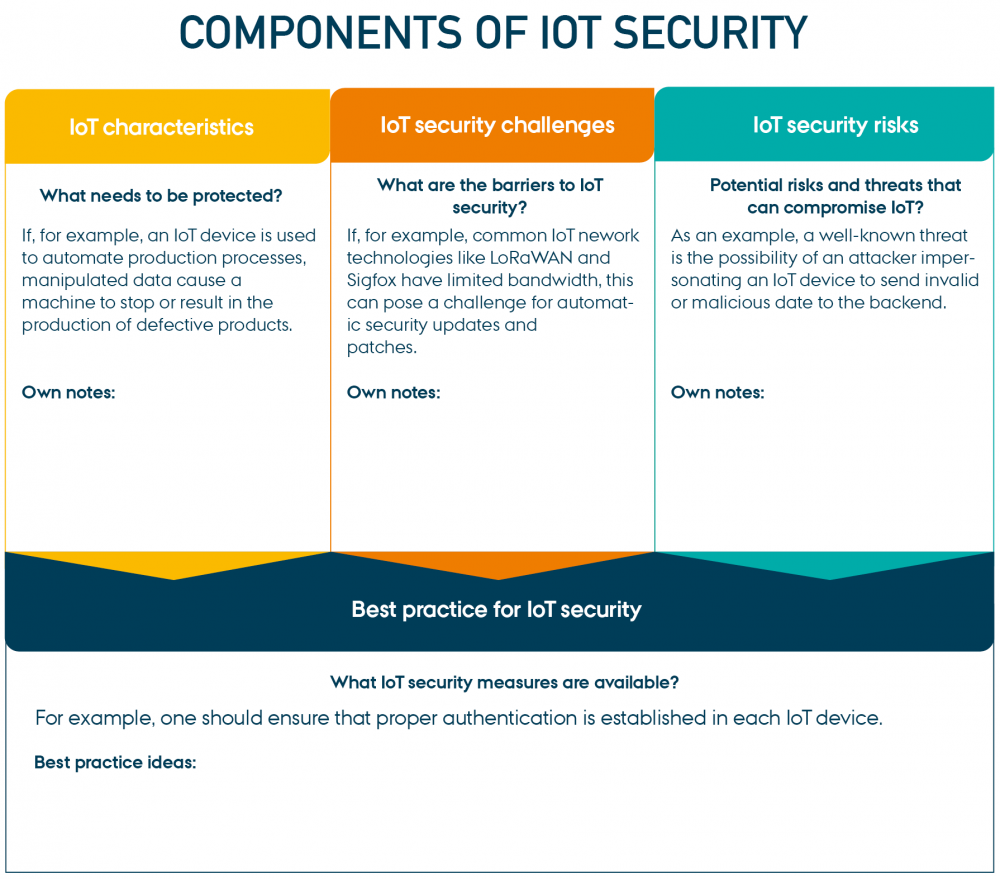
“Components of IoT security” by CyPro under licence CC BY-SA 4.0
Components of IoT security
Printable version of the tool in large format
IoT characterstics
The Internet of Things (IoT) typically includes the following characteristics:
Connected devices: IoT refers to a network of physical devices, such as sensors, actuators, and other types of equipment, that are connected to the internet and can communicate with each other and with other systems.
Network connectivity: For devices to be part of the IoT, they must be connected to a network that allows them to communicate with each other and with other systems. This may involve using wireless technologies, such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, or wired technologies, such as Ethernet or cellular networks.
Data collection and analysis: IoT devices collect and transmit large amounts of data, which can be used to gain insights and make decisions. This may involve using analytics tools and techniques, such as machine learning or data mining, to process and analyse the data.
Control and automation: IoT systems can be used to control and automate processes, such as by adjusting the settings on a connected device or triggering a particular action based on the data collected by the device.
IoT security challenges
The widespread use of the Internet of Things (IoT) entails a number of security challenges, including:
Lack of security measures: Many IoT devices are not designed with security in mind, and do not have built-in security features such as strong authentication or encryption. This makes it easy for attackers to gain access to these devices and exploit them.
Poorly designed networks: Many IoT networks are not designed with security in mind and may not have adequate protections in place to prevent attacks. This can make it easy for attackers to gain access to the network and compromise the devices on it.
Inadequate updates and patches: Many IoT devices do not receive regular updates and patches to fix security vulnerabilities. As a result, these vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain access to the devices.
Lack of user awareness: Many users are not aware of the security risks associated with IoT devices and may not take adequate precautions to protect themselves and their devices. This can make it easy for attackers to exploit these devices.
Inadequate regulation: There is often a lack of regulation and standards in the IoT industry, which makes it difficult to ensure that IoT devices are secure and properly managed. This can create a challenging environment for securing IoT devices.
IoT Security Risks
There are several security risks associated with Internet of Things (IoT) devices, including:
Unauthorized access: Attackers may be able to gain unauthorized access to IoT devices, either by exploiting vulnerabilities in the device itself or by gaining access to the network that the device is connected to. Once they have access, attackers can exploit the device for their own purposes, such as by using it to launch attacks against other devices or systems. One potential use of unauthorized access to IoT devices is spoofing, or the act of impersonating a legitimate device or user to gain access to sensitive information or disrupt operations. For example, a hacker could use a spoofed device to gain access to a network or system or could use a spoofed identity to trick other users into divulging sensitive information.
Data breaches: IoT devices often collect and transmit large amounts of data, and if this data is not properly secured, it can be intercepted and stolen by attackers. This can lead to data breaches that expose sensitive information, such as personal data or financial information.
Physical damage: In some cases, attackers may be able to use IoT devices to cause physical damage, such as by manipulating the settings on a connected thermostat or security system. This can pose a serious risk to people and property.
Privacy violations: IoT devices can collect and transmit large amounts of personal information, and if this information is not properly secured, it can be accessed and used by attackers for malicious purposes. This can lead to privacy violations and may violate laws and regulations governing the use of personal data.
Overall, the security risks associated with IoT devices can be significant, and it is important for individuals and organisations to take steps to protect themselves and their devices from these threats.
Best Practices for IoT security
Users and manufacturers of IoT devices should follow these best practices to enhance security and prevent vulnerabilities in the devices:
Users of IoT devices
These best practices to enhance security in IoT devices apply to users of IoT devices:
- Use strong and unique passwords: Use complex passwords that are difficult to guess and avoid using personal information such as your name or birth date.
- Keep software and firmware up to date: Make sure to regularly update the software and firmware on your IoT devices to ensure that you have the latest security patches and features.
- Enable two-factor authentication: Use two-factor authentication (2FA) to add an extra layer of security to your device. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as using a code sent to your phone or email.
- Use a secure network: Use a secure, encrypted network to connect your IoT devices. Avoid using public WiFi networks, as they are generally less secure.
- Protect against physical attacks: Physical attacks on IoT devices can be just as harmful as digital attacks. Protect your devices by keeping them in a secure location and using physical security measures such as locks or tamper-resistant seals.
- Follow manufacturer recommendations: Follow the manufacturer's recommendations for securing your device. This may include disabling unnecessary features, using specific security settings, or using certain types of security software.
- Educate yourself: Stay up to date on the latest IoT security threats and best practices. This can help you identify potential vulnerabilities and take steps to protect yourself and your devices.
By following these best practices, consumers can help ensure the security of their IoT devices and protect against unauthorized access and other security threats.
Manufacturers of IoT devices
These best practices to enhance security in IoT devices apply to manufacturers of IoT devices:
- Build security into the design: Incorporate security measures into the design of the device from the start. This can include using secure communication protocols, implementing encryption, and using hardware-based security measures.
- Use secure development practices: Follow secure development practices when building and testing the device. This can include using secure coding practices, conducting security reviews, and testing, as well as following industry standards and guidelines.
- Provide secure default settings: Use secure default settings for the device and provide clear instructions on how to change them if necessary. This can include using strong and device specific default passwords and disabling unnecessary features.
- Provide guidance on secure usage: Provide guidance to users on how to securely use the device, including recommendations on how to create strong passwords and keep the device and its software up to date.
- Encourage the use of two-factor authentication: Encourage users to enable two-factor authentication (2FA) to add an extra layer of security to the device. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as using a code sent to the user's phone or email.
- Provide timely security updates: Regularly release security updates to fix vulnerabilities and protect against new threats.
- ETSI TS 103 645 and EU regulation on Radio Equipment directive and guidelines for securing IoT devices
- Follow industry standards and guidelines: Follow industry standards, such as ETSI TS 103 645 and EU’s regulation on Radio Equipment directive and guidelines for securing IoT devices, those published by organizations like the IoT Cybersecurity Foundation.
By following these best practices, device manufacturers can contribute to enhancing the security and protect IoT devices against unauthorised access and other security threats.
Next steps
As we gain more knowledge about IoT security, it is important to address the risks and vulnerabilities that can affect IoT devices and systems. One effective way to do this is to conduct a risk assessment which helps you identify, evaluate, and prioritise potential risks to the system. By conducting a risk assessment, you gain a deeper understanding of specific threats and vulnerabilities that can affect your system, the likelihood of them happening as well as their consequences.

The contents described above have been developed in the project:
’CyPro – Cybersecure manufacturing in Denmark’ by Aarhus University, Alexandra Institut, DAMRC, UGLA Insights and FORCE Technology funded by The Danish Industry Foundation. Material from the project is published under licence CC BY-SA 4.0
CyPro
You have completed the entire building block
Get your certificate for this completed building block. Request the certificate and we will send you the personal certificate.



